Understanding the inventory control process: methods and best practices

Inventory is the main asset of any retail business. Effective inventory management and control helps businesses stay profitable, maximize revenue, use inventory efficiently, avoid overstocks, and reduce the number of write-offs. What is inventory control?
Inventory control can sometimes be synonymous with inventory management, as both management and control help maintain the financial stability of a business and meet customer demand.
It is a complex chain of operations that controls the storage, replenishment, classification, storage, circulation, and tracking of products. Inventory control is a multifunctional and multi-level process.
Inventory control: elements and functions
The main functional aspects of the inventory management system include:
- specification of goods, their identification numbers and types;
- storage of information on serial numbers of goods;
- implementation and control of barcodes;
- prioritization of goods by ABC analysis;
- the process of replenishment of stocks;
- management of the inventory list;
- real-time warehouse reports;
- real-time tracking of the location of goods;
- inventory storage control;
- accounting and tax operations related to warehouse management;
- synchronization of warehouse stocks with sales.
What is the importance of an inventory control system?
If a business does not control its inventory, it can lead to order delays or overstocks, which is risky for financial performance and customer loyalty. Inventory overstock is a collection of unsold goods that freezes operating capital and eventually becomes “dead” inventory to be written off or liquidated. A shortage of goods leads to customer dissatisfaction because the seller cannot provide them with the desired goods in a timely manner. If inventory control is implemented correctly, a business has full control over its inventory management.
By optimizing inventory control processes, businesses can also streamline supply chain processes, reducing logistics, storage, and transportation costs.
Methods of inventory control
So, the main functions of inventory management systems are clear: they help retailers to spend money on replenishment of stocks efficiently, as well as to increase cash flows through rational internal control over the warehouse. Let’s talk about the main methods used by these systems:
1) EOQ или Economic Order Quantity
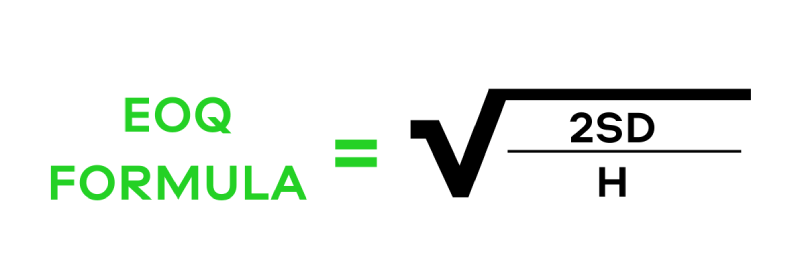
This formula calculates the required amount of inventory using the following indicators:
Q is the economic order quantity (units);
S – order value per purchase;
D – demand in units;
H – cost per unit of goods.
2) Reorder time formula
While the economic order quantity formula indicates the cost-effective amount of inventory required, the reorder time formula calculates the correct time to order an item:

Hour for order fulfillment + reserve stock = hour of rebooking
You need two indicators: order fulfillment time and safety margin.
Lead time is the number of days it takes for the goods to be delivered to your warehouse after you place an order with the supplier. For companies operating in the Chinese market and shipping their inventory from China, this indicator is crucial. When we talk about routine regular orders, imagine how important it becomes during any logistical disruptions, strikes, demand surges, or seasonal deliveries.
To calculate the need for lead time, multiply two numbers: the lead time for a particular item and the average daily consumption of that item.
Safety stock is a “cushion”, a buffer of available goods in your warehouse. To calculate it, multiply the highest (maximum) daily consumption of an item and the highest lead time for that item (in days). Then multiply the average daily consumption of the item and the average lead time (in days). Finally, subtract the last number from the first. Voila, this difference is your safety stock in units.
Example: You sell cell phone cases and accessories in the United States. Your supplier is based in China. Usually, it takes 30 days to deliver your goods from China to the US (this is the average lead time). But sometimes, during holidays, demand surges, strikes, etc., it takes 50 days to deliver the goods (i.e., the longest lead time). You sell an average of 5 mobile phone cases per day (this is your average daily consumption), and the highest sales level you see during Black Friday or holiday periods is 10 mobile phone cases per day (this is your highest daily consumption). So, your safety stock formula looks like this: 10×50 – 5×30 = 500-150 = 350 (units)
It is important that effective inventory control requires a combination of these two methods, both EOQ and reorder time.
One of the advantages of inventory management systems is that they perform these calculations automatically, and all you have to do is turn on notifications – the system will automatically notify you of the reorder time and quantity.
Inventory control practices and KPIs
The right key performance indicators (KPIs) are fundamental to effective inventory management, as they determine future productivity and profits. Most KPIs are related to inventory as the main asset of a retail business and to sales as the end result in retail.
It is also important to understand that many KPIs “blur” the meaning of each one individually, and moreover, they do not give a complete picture. Therefore, it is worth determining both the quality and quantity of KPIs in each area of the business you manage.
Typical indicators for inventory management:
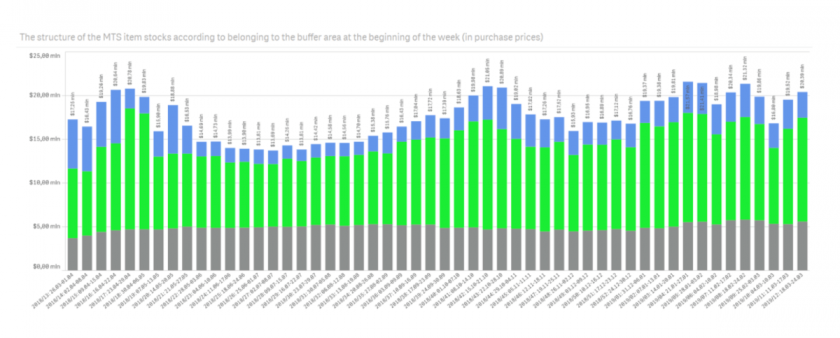
1. Inventory costs
This gives a general idea of the company’s investment in inventory at the moment and over time. In addition to tracking this indicator at the moment and over time, an assessment of the inventory structure demonstrates how much the company is spending in terms of safety stock, inventory, overstock, and actual inventory for sale.
Below are examples of the inventory structure of two grocery retailers (gray area – safety stock and shelf stock, green area – stock for sale, purple area – excess stock):
2. Sales
Sales in purchase prices (cost of sales) and sales prices. In fact, everyone in retail works on sales. As for category management, sales are analyzed by category in terms of outlets, suppliers, and other analytics.
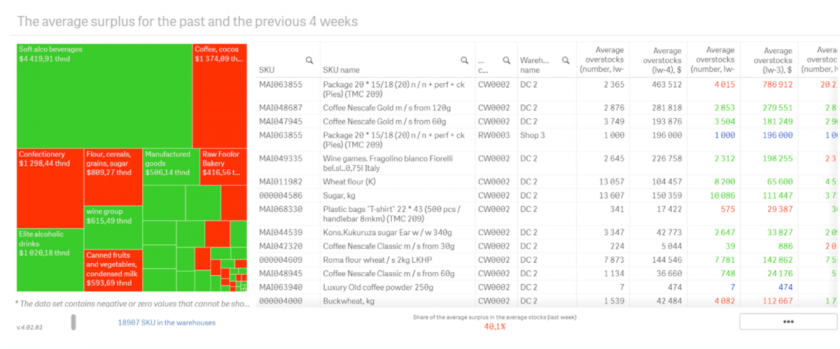
3. Overstock
Displays the % and value of inventory that was formed as a result of an increase in orders or a significant drop in consumer demand. In addition to the overstock itself, it is also worth evaluating how long this overstock has been in the store or warehouse.
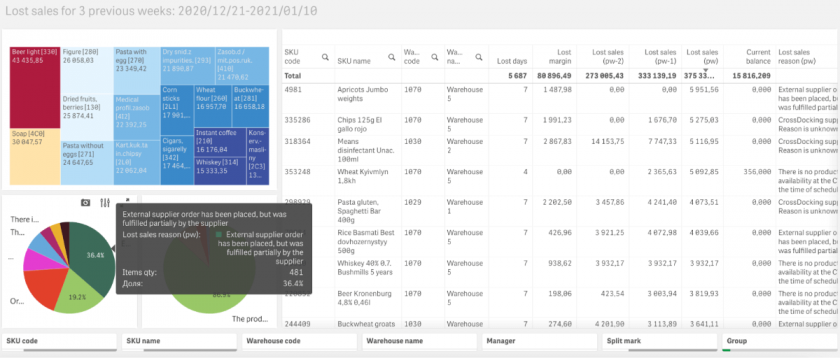
4. Lost sales
The ABM Inventory system has a special report on statistics and reasons for lost sales, which shows changes in the dynamics of the indicator both for a separate category of goods and by groups.
5. Service level
6. Inventory to sales ratio
To summarize, the above KPIs have the potential to increase retail profitability and provide clarity on operational performance in a constantly changing environment.
Implementation of inventory management software in business
Every business is unique, with its own individual needs, KPIs, goals, and strategies. Methods and ways to control inventory vary, but they are all acceptable. The use of each method depends on the size, model, policies, and financial goals of your business. You can combine different methods in your strategy, but keep in mind that switching between inventory control methods too often can have a negative impact on financial reporting, accounting, and analytics because different methods use different approaches and principles.
This step-by-step plan will walk you through the basics of implementing an inventory control system in your company. So, to get started:
1. Define your goals and objectives
When it comes to inventory, the turnover rate is one of the most common, important, and useful indicators that shows how many times inventory is sold in a year/quarter/etc. To set ideal inventory turnover goals, you should take into account benchmarks in your industry and calculate the profit margin for all inventory and each SKU.
There are several other metrics to consider and track, such as inventory storage cost, inventory sales per day, inventory to sales ratio, etc.
2. Get your warehouse in order
Effective warehouse management, including the movement, transfer, and storage of goods, is one of the most important elements of inventory management. It’s all about common sense – if your warehouse is messy or your products are randomly placed, you’re unlikely to be able to ensure a steady flow of sales, deliveries, and inventory movement. Consider a cyclic inventory as a way to count inventory and control the quantity of goods.
3. Invest time and effort in product labeling and categorization
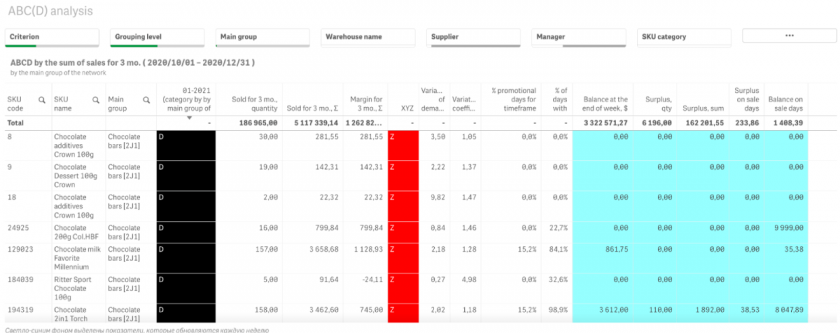
If products are hard to find and identify, you’ll need more labor and more time for order fulfillment and logistics. If products are searched for and the in-and-out movement is controlled manually, the possibility of human error increases. To remain cost-effective and reduce the impact caused by human error, create a convenient and easily classified system for all your goods and products. The ABC method of inventory classification and analysis, based on product profitability and sales value, is one of the most effective options to consider.
4. Keep up with new inventory management technologies
Some small business owners perform control using Excel spreadsheets with 2-3 functions and fill in all warehouse data manually. Manual inventory control requires an investment in human capital, as a person is responsible for recording even the smallest movements of goods, keeping track of product names, types, locations, quantities, etc.
In contrast, automated inventory control systems can perform these functions in seconds, saving time and money. New technologies can automatically prevent overstocking and unfinished orders, track customer demand and level inventory levels accordingly, predict the next warehouse order by analyzing sales and product movement, manage warehouse and barcode systems, and even analyze future sales trends.
Based on the many years of experience of our customers from various retail sectors, we have analyzed all the weaknesses of the business and created the most effective inventory management system – ABM Inventory.
This cloud-based solution will help you quickly and accurately identify areas that require special attention. This will help you optimize orders and delivery in the shortest possible time, which will lead to the successful implementation of the company’s further development strategy.
In addition, with the ABM Inventory system, you can minimize the human error factor when placing orders, relying solely on accurate data obtained as a result of complex algorithmic calculations to determine the real need for a separate SKU at each point of inventory storage.
Conclusions
Always remember to use a properly integrated inventory management system in your business. Forecasting demand, keeping records of warehouse data, and replenishing stocks on time is a tedious job that requires accurate planning.
An inventory management system is designed to help you: it not only ensures stable cash flow, inventory management, barcode scanning system efficiency, and customer satisfaction, but also maintains relationships with suppliers and synchronizes all warehouse processes.